The Fourier and Laplace Transforms
In this post I want to briefly cover the basics of the time and frequency domains and how we can switch between them with the Fourier and Laplace transforms.
The Fourier Series is used to describe a signal as a sum of sinusoidal components. Each sinusoid must be a multiple (harmonic) of the smallest component sine wave [1].
A Fourier Transform is the continuous version of the discrete series and is used to convert a signal from the time domain to the frequency domain. It can represent any signal, continuous or not, as an infinite summation of sinusoids [1]. We can write the equation as shown below. It is also worth noting that e raised to an imaginary power can be written as the sum of a cosine and an imaginary sine per Euler’s formula [1]. That is how the Fourier Transform incorporates sinusoidal waves into its operation.
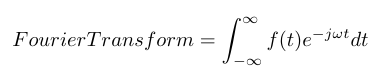
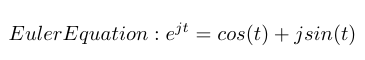
The Fourier Transform is a general approach to describing a linear system based on its frequency response [1]. But it is limiting because we generally describe phenomena in engineering as differential equations, and differential equations possess both sinusoids and exponential components [1]. For example, if you think of a spring-mass-damper system, it has the following differential equation and associated solution:
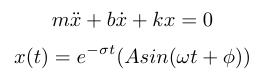
We can describe second order systems as a sinusoidal wave contained inside an envelope described by an exponential term. The exponential term describes how the damper reduces the energy of the system. In order to convert this system to the time domain, we have to adjust the Fourier Transform equation [1]. Specifically, we know the real world is causal, so we start from t = 0 because starting from negative infinite time does not make any sense [1]. We also add a term for exponential component of the signal. Then we can combine the information about the exponential with the information about the sinusoids, and derive the frequency variable, s [1].
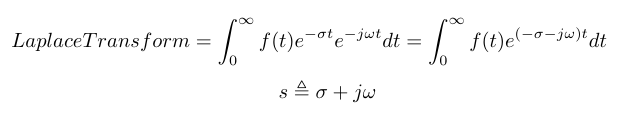
References
[1] Douglas, Brian. “Control Systems Lectures - Time and Frequency Domain.” https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=noycLIZbK_k&list=PLUMWjy5jgHK1NC52DXXrriwihVrYZKqjk&index=3 Visited on 08/13/2019.
